Computational aids for architects for early design phases
Computational aids for architects for early design phases
I explored the explainability of auto-completion tools for spatial layouts in early architectural design phases.
In the next thirty years the world population is expected to approach the amount of ten billion people (Statista Research Department, 2020), posing a huge challenge on the construction industry. In order to meet the housing requirements of the future, the architects need to work in a faster and more efficient manner without compromising the architectural quality.
The aim of my master thesis is to explore if additional information can support architects in understanding suggestions of a hypothetical intelligent design assistant like WHITE BRIDGE and reduce the cognitive workload of design decision in early design stages. Furthermore, the influence of the representation of this information on the visually driven target group is examined through the mixed methodology of triangulation, derived from social sciences. The used triangulation consists of literature research and a user study. The theory-driven explanations and explanation visualisations are based on the framework of Wang et al. (2019), as well as a literature review of architects’ design decision making process, workflow and architectural quality assessment. The user study is conducted with working architects, utilising a digital paper prototype created from the theoretical research.
The results show that the cognitive limits of the architects are expanded by the explanations, while the visualisation methods significantly influence the usefulness and utilisation of the conveyed information within the explanations. The architects themselves identify opportunities for using a hypothetical intelligent design assistant. In order to make well-informed decisions, they seek even further support in terms of visualised explanations for the suggestions and the visibility of choice. Thus, the architects are supported, while ensuring a sense of ownership over the design decisions.
Statista Research Department. (2020, April 22). Prognose zur Entwicklung der Weltbevölkerung von 2010 bis 2100 (in Milliarden). Retrieved April 10, 2021, from https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/1717/umfrage/prognose-zur-entwicklung-der-weltbevoelkerung/
Wang, D., Yang, Q., Abdul, A., & Lim, B. (2019). Designing Theory-Driven User-Centric Explainable AI. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1–15). Association for Computing Machinery.
![WHITE BRIDGE in use [render]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/60da039c1549bb10ed641f7d/df6b7c06-a823-4a48-b313-097cc641d6c3/ComputationalsAidsF.png)
WHITE BRIDGE in use [render]
explainability for an intelligent design assistant

WHITE BRIDGE icon
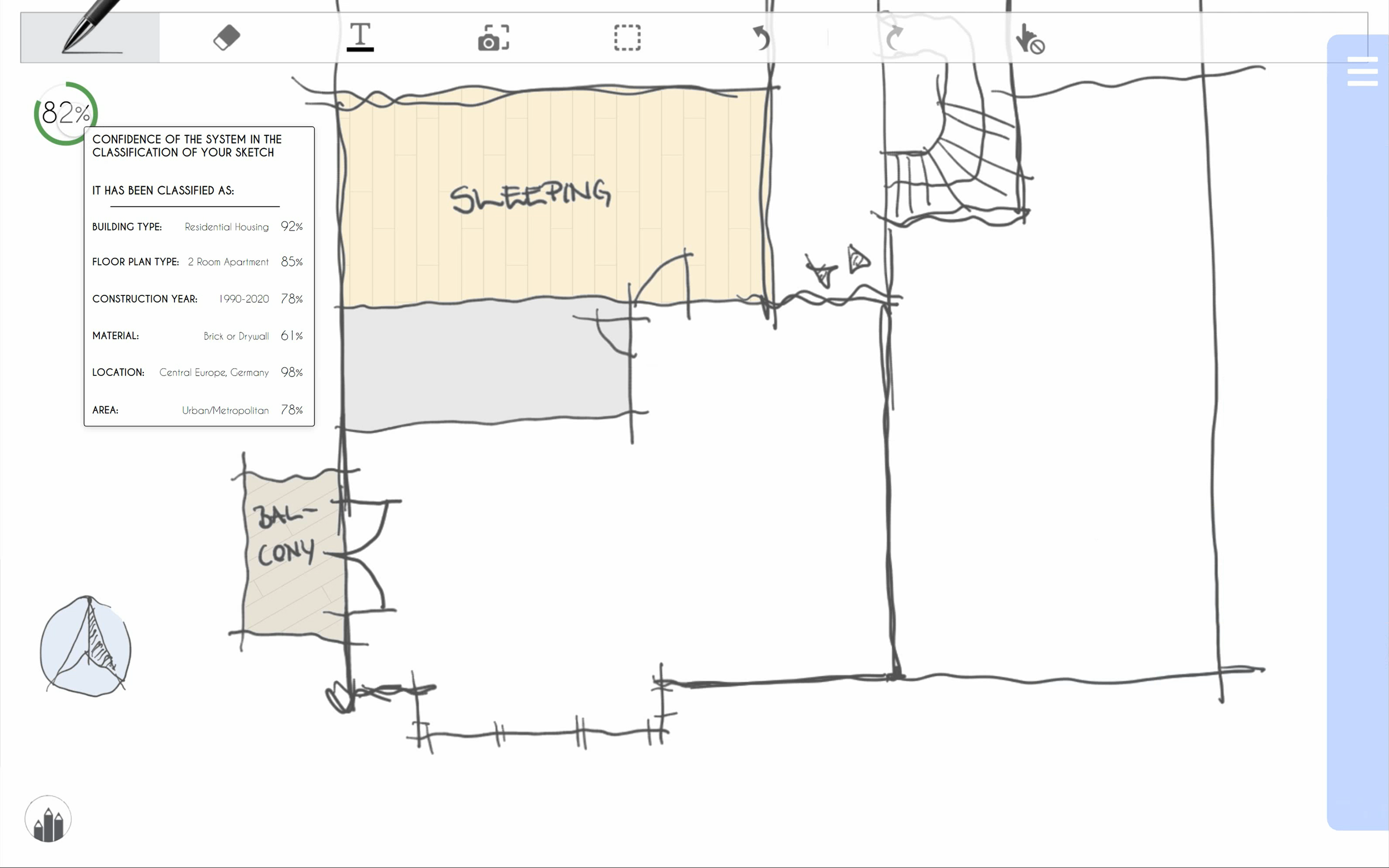
WHITE BRIDGE identified rooms and has suggestions ready
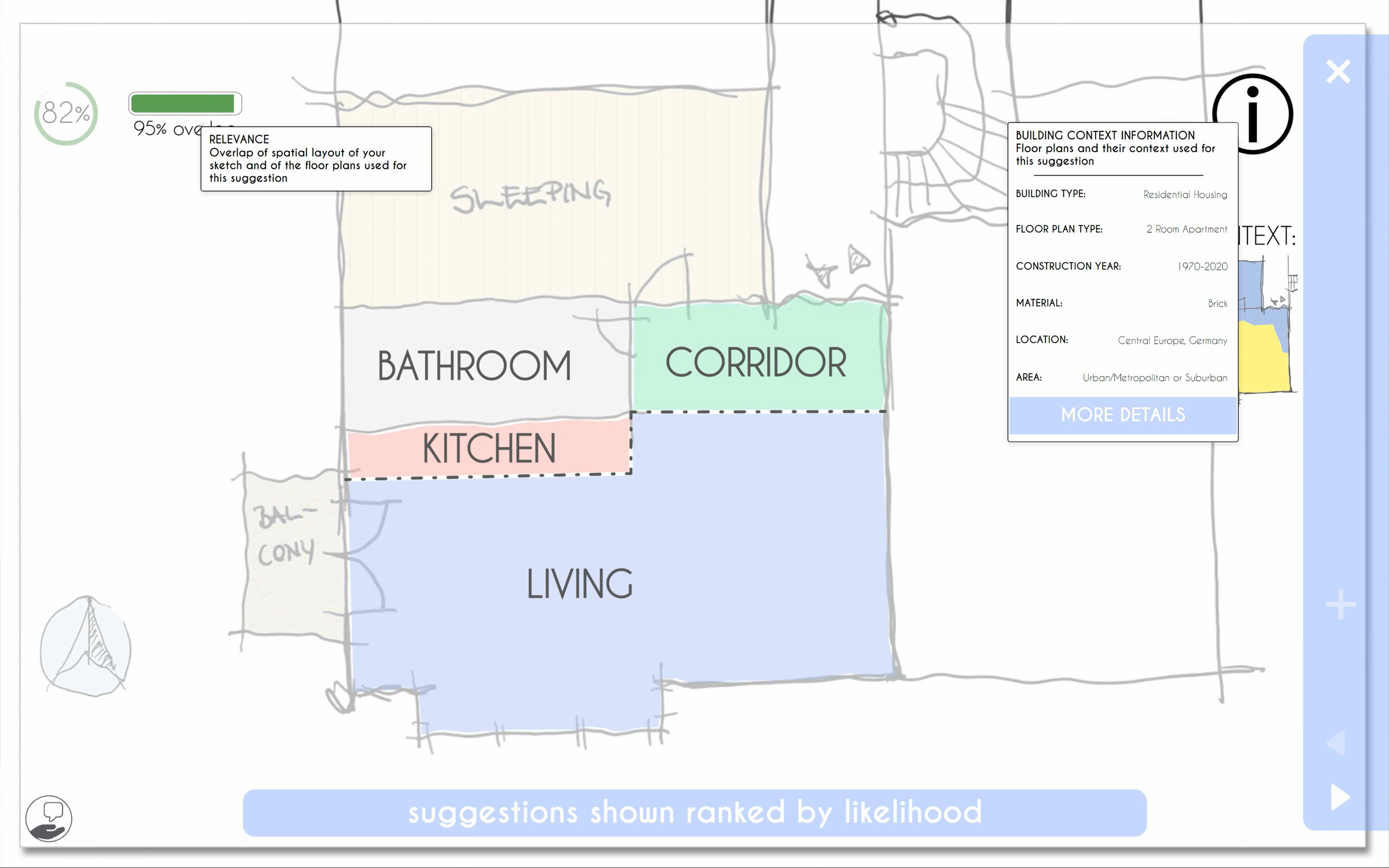
suggestion view with open tooltips of explanation visualisations for supporting the architect and mitigating biases
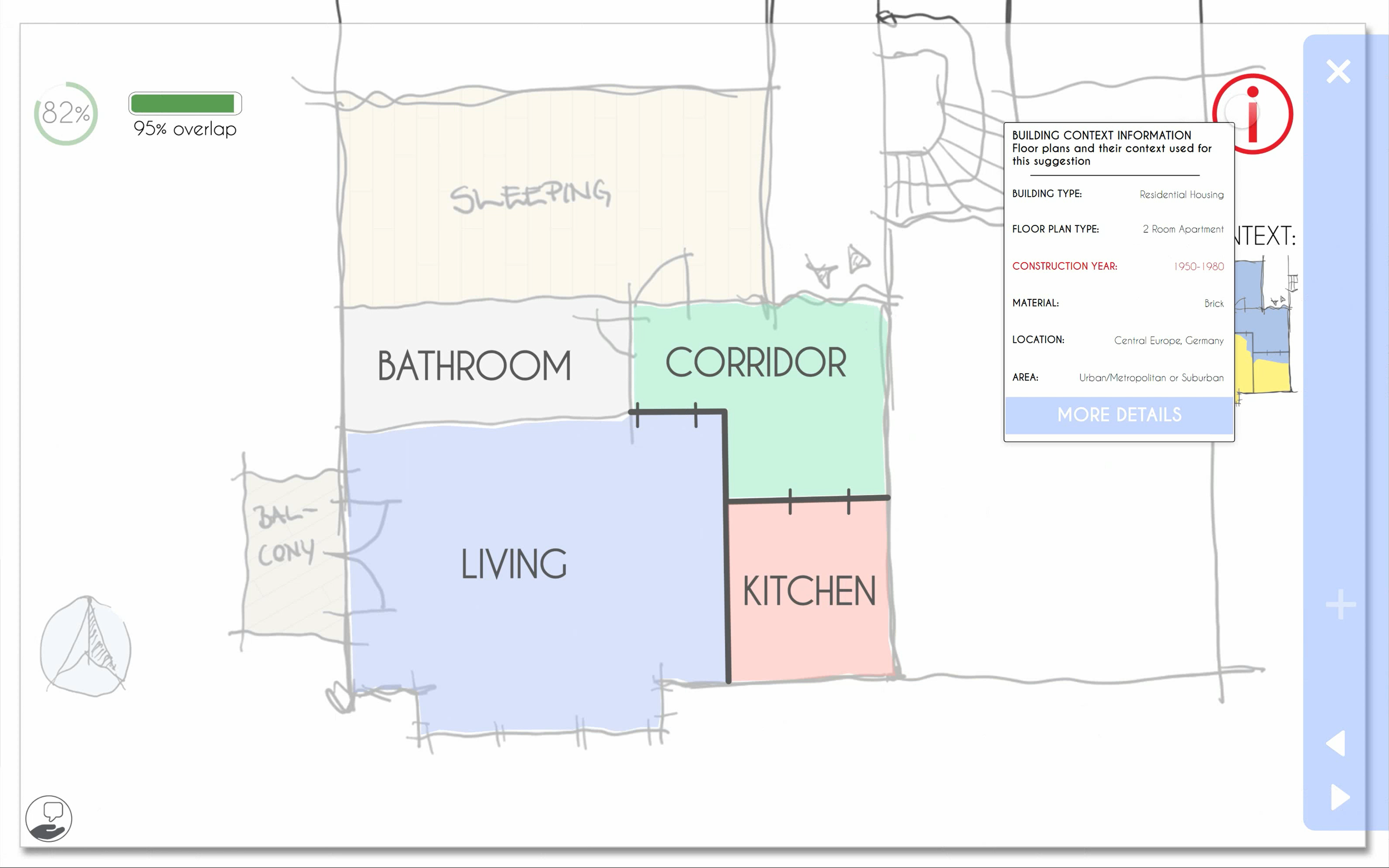
suggestion view with open tooltips of explanation visualisations with red alert for divergence
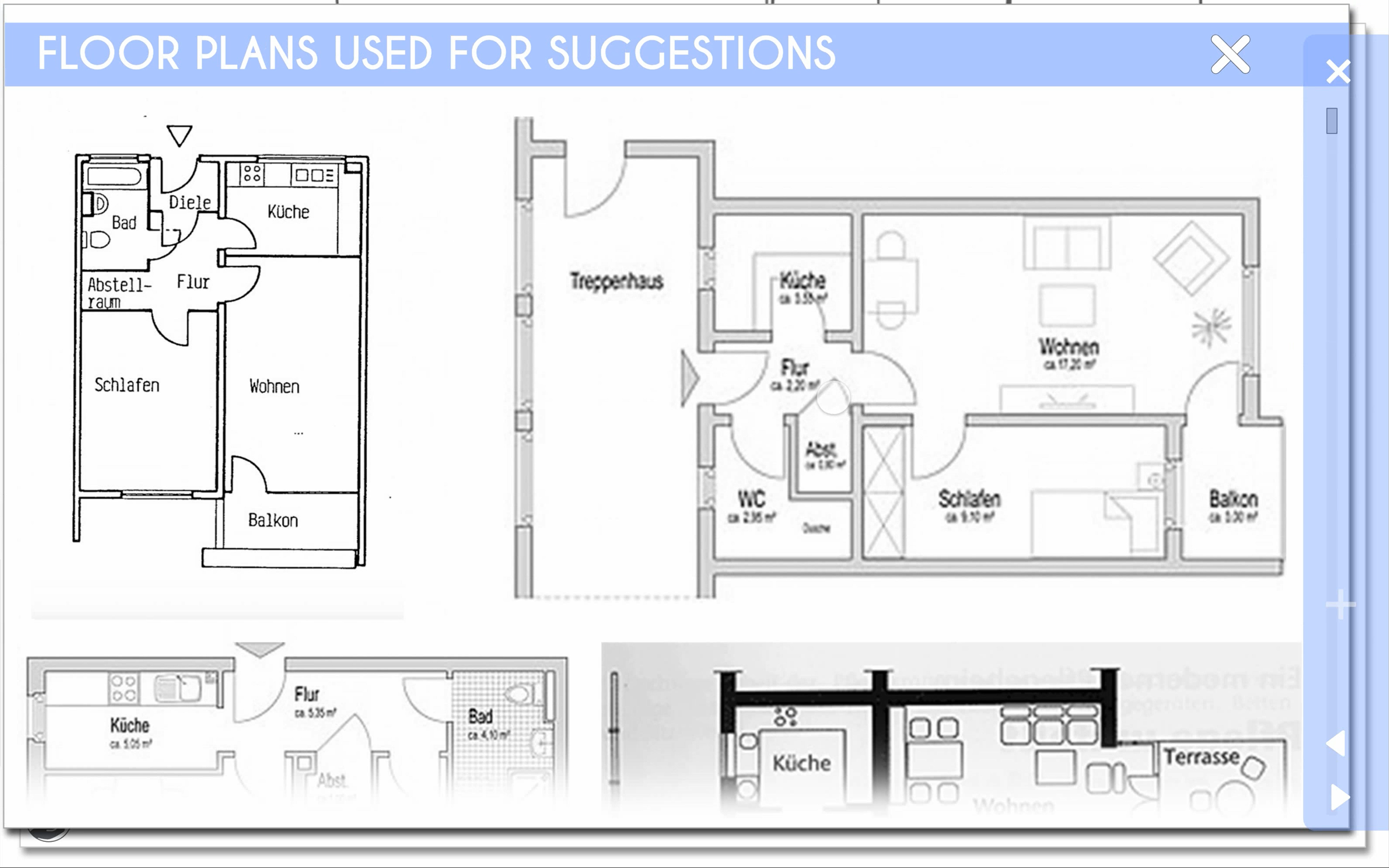
access to the floor plans used to create the respective suggestion
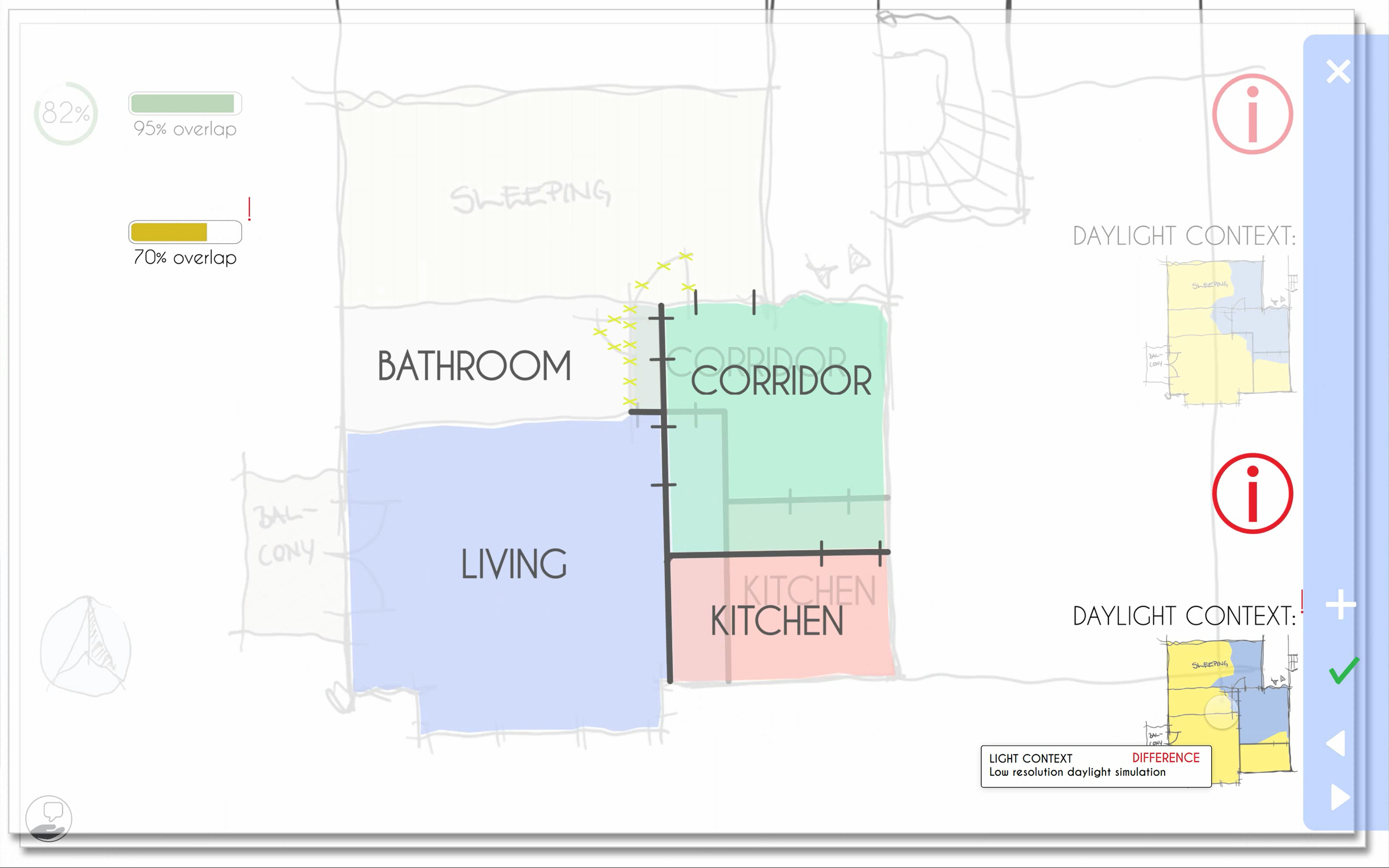
two different suggestions layered on top of each other for better comparison
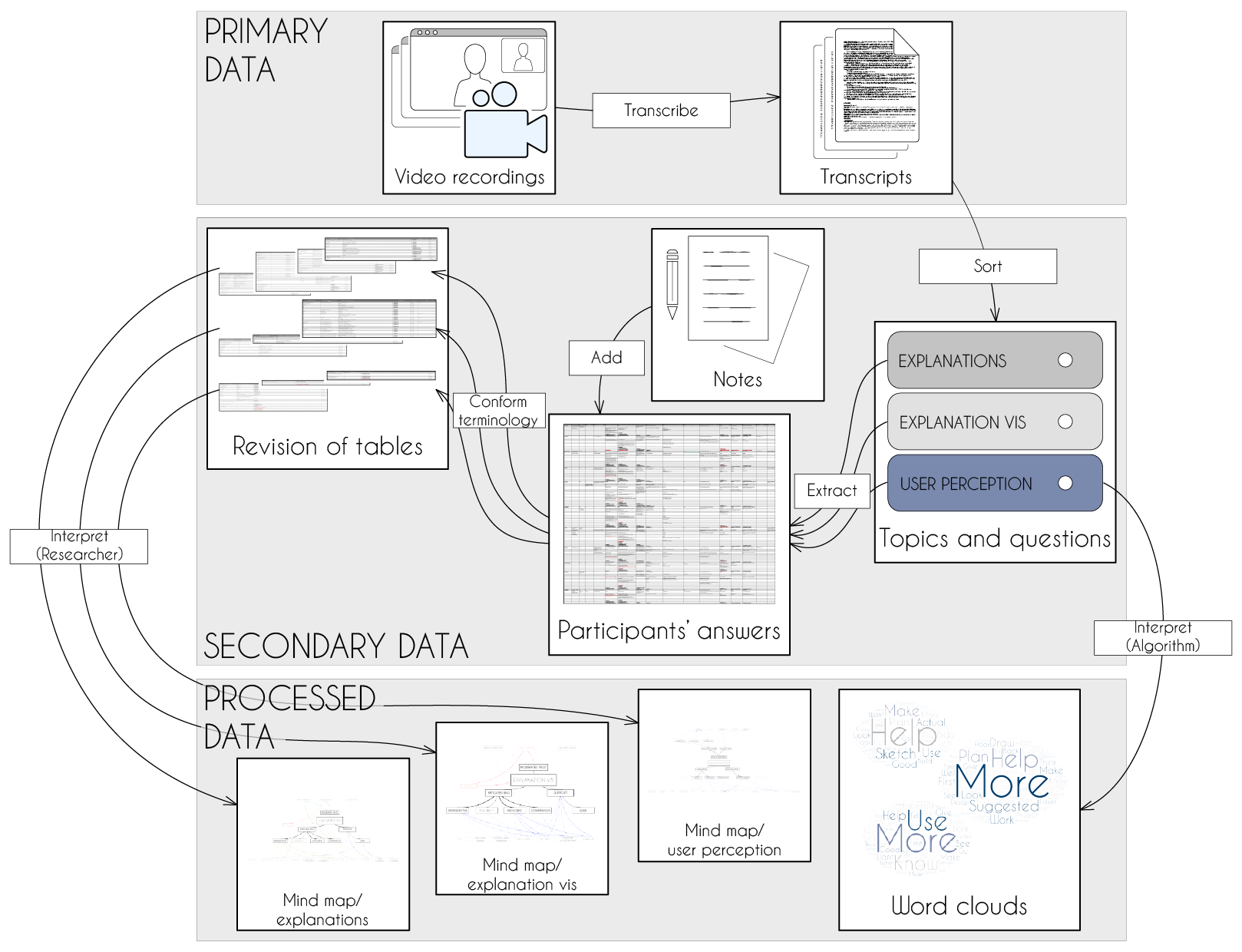
data collection and analysis process
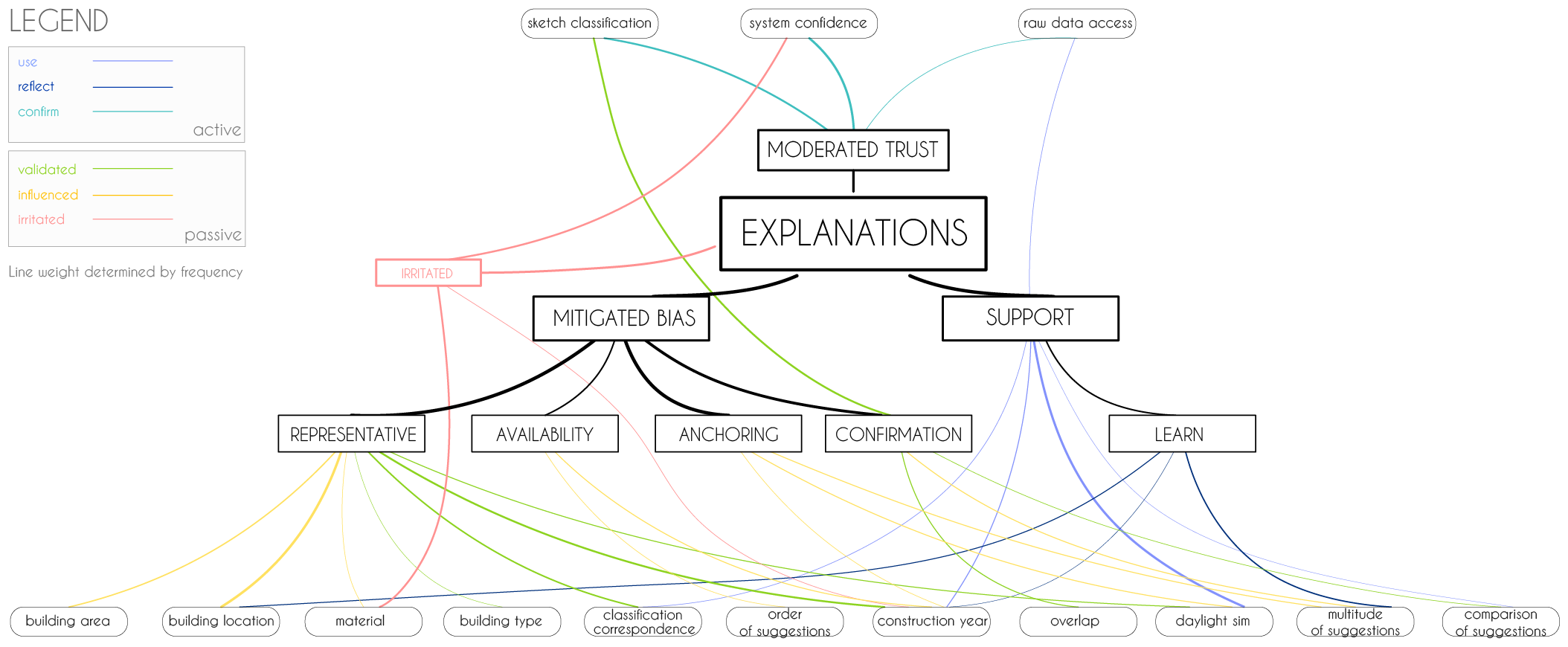
'explanation' mind map
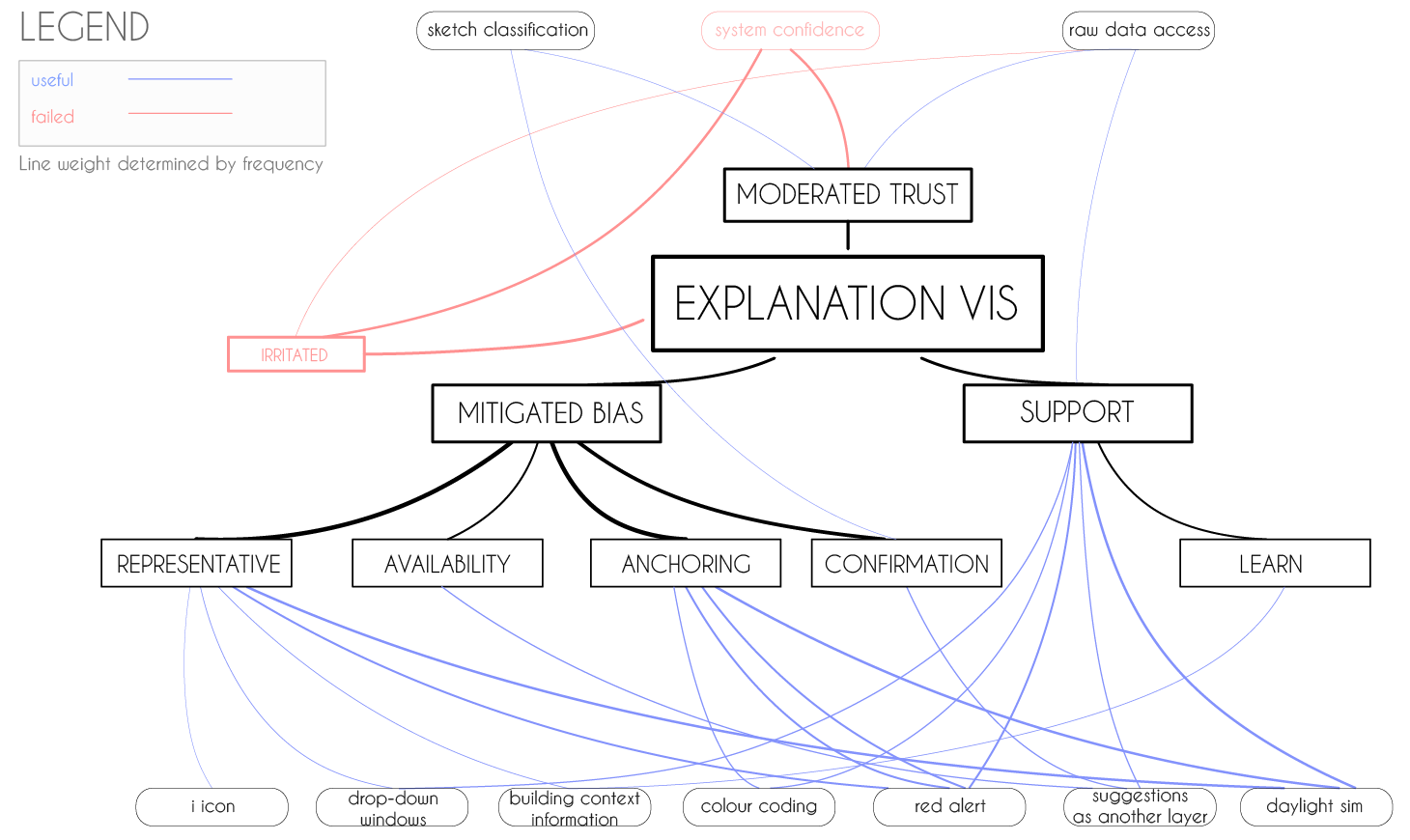
'explanation visualisation' mind map
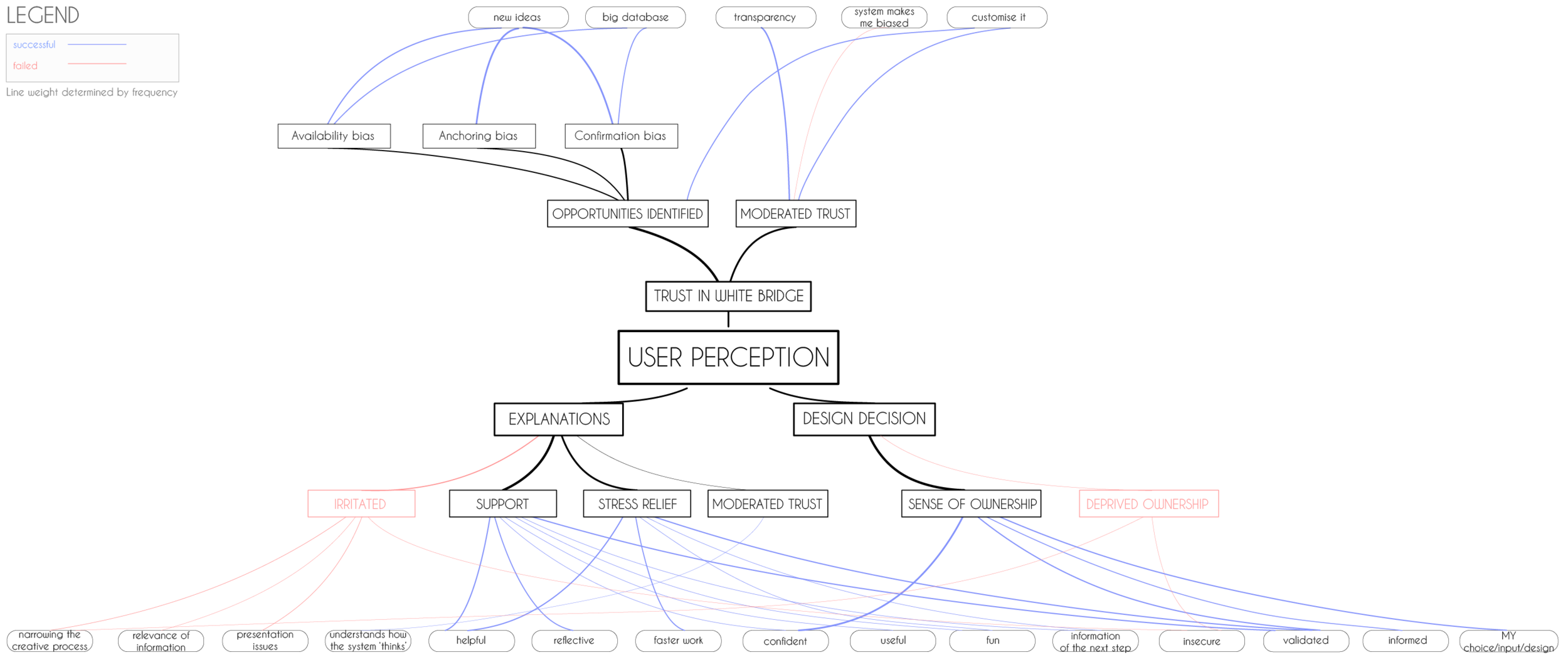
'user perception' mind map

'user perception' word clouds
